In electrical engineering, the Power Factor (PF) is a ratio of the real power measured in watts absorbed by the load to the apparent power measured in volt-ampere flowing in the AC (alternate current) circuit. Power factor is a dimensionless number in the closed interval of -1 to 1, this means the value will always be less than 1.
FYI: In a DC (direct current) circuit the PF is always one, just one, and never anything but one.
How to calculate PF?
To calculate PF of a machine you need to identify its watts and volt-amps.
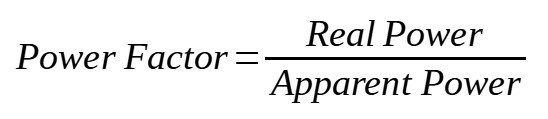
Power Factor = Real Power (in watts) / Apparent Power (in volt-amps)
Let’s calculate the PF of an inverter I have in my house. Luminous NXG 1400 rated with 900 VA while it can handle a load maximum of 720 watts (it beeps above this). Power factor = 720 Watts / 900 VA = 0.8 or we can say 80%.
This means my solar inverter has a PF 0.8, or 80% efficient in handling everything.
Leave a Reply