A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a network of computers which caches and delivers web content over different geographical locations.
CDN is a means through which websites can more efficiently deliver web content to their visitors through an intricate web of servers that handle cache duties.
Someone is not wrong in calling CDN as Distribution Networks simply because that does a good job of summing up their role.
In CDN, not only one server used to handle the world’s traffic but different cache servers are also used to serve the content.
Such cache servers located all around the world and every cache server handles its surrounding country’s traffic. Use of CDN results in a low, ultra-fast latency of the connection established between the server and the visitor’s computer.
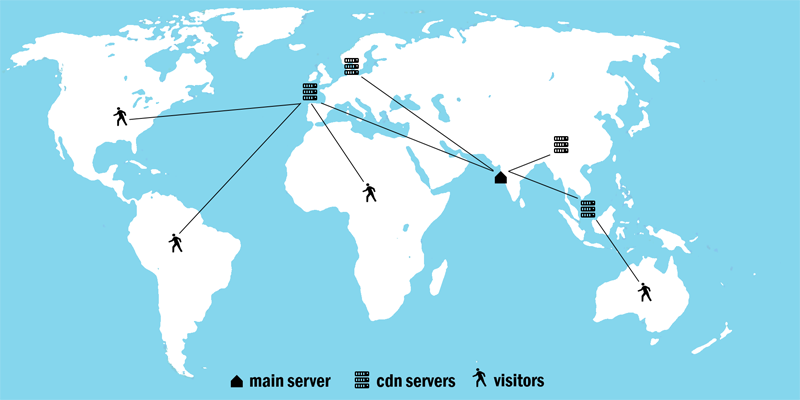
Let’s say if you are using a content delivery network for your website; where your main server is in India and your CDN services allow you cache servers in Singapore, China, Amsterdam, and London.
In this case, if an American user is trying to load your website so he would be connected to the London server which has the lowest latency and the contents would be transferred from London. If anyone tries to reach your site from Australia so the Singapore server will serve the contents for him.
See below the map to understand how the CDN works actually.
A CDN service can generally reach even thousands of servers from which websites can draw data. Content that is handled by CDN providers is available as multiple copies that are located on multiple servers.
These servers are obviously not located close to one another, but rather far away. This helps tremendously when website visitors request that content.
So let’s say that, for example, that a visitor opens up a page that contains an image. The information pertaining to that image is drawn from the CDN server located closer to the visitor’s PC. This allows for the information to be transferred much faster than if it would be coming from the other edge of the world.
By deploying the same data from the server closest to the target PC, websites are able to load a lot faster and efficiently. That means a whole static copy of the main server is available with CDN servers, so if suddenly any country started bombarding on your website for any famous content then they will not hit your main server but will hit the CDN server of that location.
Let’s see what could be the advantages and disadvantages of using CDN services.
Advantages of CDN
- You can handle more numbers of traffic as it spreads the burden of the main server to all CDN servers.
- Visitors will able to access your site’s content faster due to the lowest latency.
- There are SEO benefits too as the site becomes faster due to the nearest available servers.
- You may enjoy 100% uptime because most of the CDN services work on a collaboration basis; that means if one server failed to deliver your content, another server will work for that and the chain continues.
Disadvantages of CDN
- Cache technology does not work on a live basis but on a time basis. If any content gets updated it will take some time to update the content on all CDN servers.
- For the current time using a content delivery network would be an additional cost. There are also free CDN services too.
The reason why webmasters or managers are so adamant about implementing CDN into their websites is that these services help a lot with site loading speeds and efficiency. This might seem a bit much as no one could care about website loading speed that much, right? Wrong! In this day and age, speed is a crucial asset that at times even exceeds the need for quality although that’s never recommended or preferred.
People today are looking for the fastest way in which they can get what they want and if a website takes even a few instances longer to load than they are willing to wait, they will move on and look for another website with similar content. This pressures and forces website managers to use all available tools to make websites load and function as fast as possible.
This is all about the content delivery network.
Big companies like Facebook, Google, Twitter, and Yahoo uses this technology on a mass scale to serve the contents blazing fast.
Leave a Reply